Muscle Tone
Postural tone
It defines as a certain amount of resistance to passive movements (Foster, 1980). Visco-elastic properties of soft tissue. The state of readiness of the body musculature in preparation for the maintenance of a posture or the performance of a movement (Bernstein, 1967).
Active contractile component
- Cross bridge of actin- myosin "sliding mechanism theory"
- Passive component (collagen)
- Parallel elastic components
- Series elastic components
- Tendon Comprised of white collagen
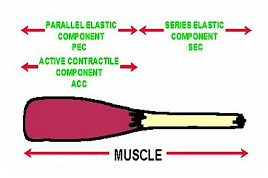 Muscle Components
Muscle Components
Normal Postural Tone enables an individual to...
- Maintain an upright posture against the force of gravity.
- Adapt to a varying and often changing BOS.
- Allow selective movement to attain functional skills.
"Postural tone is adaptable and varies throughout different parts of the body in response to desired goals (Edward, 1996)"
Components of Normal Postural Tone
- Gravity
- Center of gravity (COG)
- Base of support (BOS)
- Ground reaction force (GRF)
- Recruitment Order
- Type of Motor Units
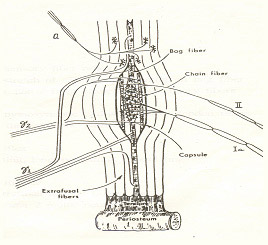
Muscle Spindle
- Structure
- spindle = connective tissue (capsule) + 2-12 intrafusal fiber(2 nuclear bags & 4-5 nuclear chains)
- intrafusal fiber vs extrafusal fiber
- nuclear bag type vs nuclear chain type
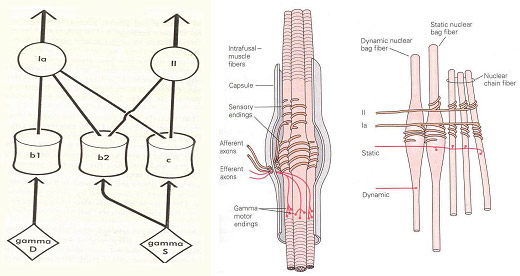
- Afferent innervation
- primary endings / Group Ia afferent fibers both nuclear bag & chain fiber. Annulospiral ending
- secondary endings / Group II fibers static bag fiber & chain fiber. Flower-spray ending
- Firing patterns
- Both group Ia & II have a good static (tonic or steady-state) response
- Both group Ia & II display spontaneous activities
- Primary endings shows more dynamic response than secondary
- Secondary endings are mainly sensitive to the length of the muscle
- Primary endings are sensitive to both changes in the length of the muscle & to changes in the rate of stretch
- Increase activity during muscle stretch but cease firing during muscle contraction
- Motor innervation to the muscle spindle
- alpha vs gamma motor neuron
- alpha motor neuron vs skeletomotor neuron
gamma motor neuron vs fusimotor neuron - Function of gamma motor neuron
- Two types of gamma motor neurons
- Gamma dynamic; innervate nuclear bag fiber
- Gamma static; innervate nuclear chain fiber
Specifically regulate the sensitivity of the spindles either to dynamic or to static phases of stretch. Level of gamma efferent discharge may influence alpha motor activity & muscle tone. Abnormal gamma activity can significantly distort motor function
Stretch Reflex (Myotatic reflex)
Phasic (dynamic) stretch reflex
- is elicited by rapid muscle stretch
- oppose sudden changes in muscle length
- rapid stretch → discharges the primary endings → group Ia afferent nerve fibers → a-motor neuron (homonymous mm)
Tonic (static) stretch reflex
- result from slower muscle stretch
- during passive movement of a joint
- same connections as the phasic reflex
- group II afferent nerve fibers
Muscle is slowly, passively stretch
→ Continuous tonic receptor signals Evoked both
→ Primary & secondary ending
→ Stimulate motor units within the muscle
→ Create a resistance to that movement
→ Muscle Tone
Functional role of g-loop
Muscle contraction can be elicited by two ways
→ Directly exciting a-motor neuron → Indrectly through g-motor neuron excitation
Gamma-motor neuron excitation
intrafusal fiber contraction → Ia fiber excitation → alpha-motor neuron excitation → muscle contraction
근방추 : 기능
근육 내 감각 수용체
다음의 변화를 모니터링합니다
- 근육 길이
- 스트레칭 속도
활성화된 사람
- 액티브 스트레칭
- 수동 스트레칭
단일 시냅스 반사
- 근육 스트레칭은 척추를 활성화합니다
- Ia 구심섬유는 알파 운동 뉴런과 시냅스를 형성합니다.
- 운동 뉴런은 근육 섬유를 활성화하여 수축을 유발합니다.
- 근육을 늘리면 보상 수축이 발생합니다.
근방추의 역할
- 근육 길이의 신호 증가
- 신경계에 정보를 제공합니다. 근육의 절대 길이 근육의 길이 변화율(속도)
- 사지 위치에 대한 인식
- 척추상부 센터에 메시지를 보냅니다.
- 근육 톤의 사전 설정 및 조절.
- 근육 수축을 조정하고 원활하게 합니다.
